Understanding THC vs. CBD for Medical Use
Cannabis, a plant with a rich history of medicinal use, contains a multitude of chemical compounds, but two stand out prominently: Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD). Both interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, influencing various physiological processes, but they offer distinct therapeutic properties and effects. This article will delve into the differences between THC and CBD, clarifying their roles in medical applications, and helping you make informed decisions regarding your medical cannabis journey. For more information on how to obtain a medical card, you can visit our application page or check out our guide on getting a medical card in Virginia (if applicable to your location).
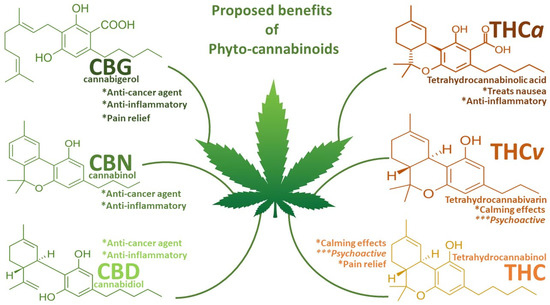
THC: The Psychoactive Cannabinoid
THC is the primary psychoactive component of cannabis, responsible for the “high” associated with marijuana use. However, its effects extend beyond mere intoxication; it holds significant therapeutic potential. THC interacts with CB1 receptors in the brain and throughout the body, which play a role in pain perception, mood regulation, and appetite stimulation. This is why THC is often used to treat chronic pain, nausea (particularly in chemotherapy patients), and to improve appetite in individuals with certain conditions. Further information on the specific qualifying conditions can be found on our state-specific pages, such as those for West Virginia, Virginia, and Florida. However, it’s important to remember that THC’s psychoactive properties may not be suitable for everyone. You can learn more about responsible cannabis use in our blog post on the cost of using medical cannabis.
Potential Benefits of THC
- Pain relief
- Nausea and vomiting reduction
- Increased appetite
- Muscle relaxation
- Sleep improvement (in some cases)
Potential Side Effects of THC
- Anxiety and paranoia
- Dry mouth and eyes
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Increased heart rate
- Impaired coordination and judgment
CBD: The Non-Psychoactive Cannabinoid
Unlike THC, CBD is non-psychoactive, meaning it doesn’t induce a “high”. It interacts primarily with CB2 receptors, which are more prevalent in the immune system, reducing inflammation and influencing immune responses. CBD’s therapeutic benefits are increasingly recognized for a variety of conditions. It’s often used to manage anxiety, inflammation, pain, and even epilepsy. To learn more about how to properly consume CBD, be sure to check out our guide on decarboxylating cannabis for optimal effects. A comprehensive understanding of the endocannabinoid system is crucial; further information can be found via links to reputable resources on the subject.
Potential Benefits of CBD
- Anti-inflammatory properties
- Pain relief
- Anxiety and stress reduction
- Sleep improvement
- Potential neuroprotective effects
Potential Side Effects of CBD
CBD generally has a good safety profile with minimal side effects, but some users report:
- Dry mouth
- Diarrhea
- Changes in appetite
- Fatigue
- Drug interactions (with certain medications) – for instance, see our blog post on Zoloft and weed interactions.
THC vs. CBD: Choosing the Right One
The choice between THC and CBD depends largely on individual needs and preferences. Patients seeking pain relief, appetite stimulation, or nausea reduction may benefit from THC, while those prioritizing anxiety reduction, inflammation management, or other non-psychoactive effects might prefer CBD. Some patients find relief in the synergy of both compounds, known as the “entourage effect,” leading them to use full-spectrum cannabis products which include both THC and CBD and other cannabinoids. For a deeper dive into this topic, you might find our article on the importance of terpenes helpful.
Remember, it’s crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before incorporating cannabis into your treatment plan, especially if you’re on other medications. They can help you determine the appropriate dosage and form of THC or CBD based on your individual health status and needs. This might also help in getting a medical marijuana card, especially in states like West Virginia, Virginia, or Florida. For more specific details on qualifying conditions and the application process in different states, you can find resources on our state-specific pages.
Conclusion
THC and CBD, while both derived from the cannabis plant, offer distinct therapeutic benefits. THC’s psychoactive effects are beneficial for specific conditions, while CBD provides non-psychoactive therapeutic advantages. Understanding these differences is vital for making informed decisions regarding medical cannabis treatment. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach for your individual needs. Remember to explore our other resources, such as our blog post on the cost of medical cards, to further your understanding of this powerful plant’s medicinal potential.
